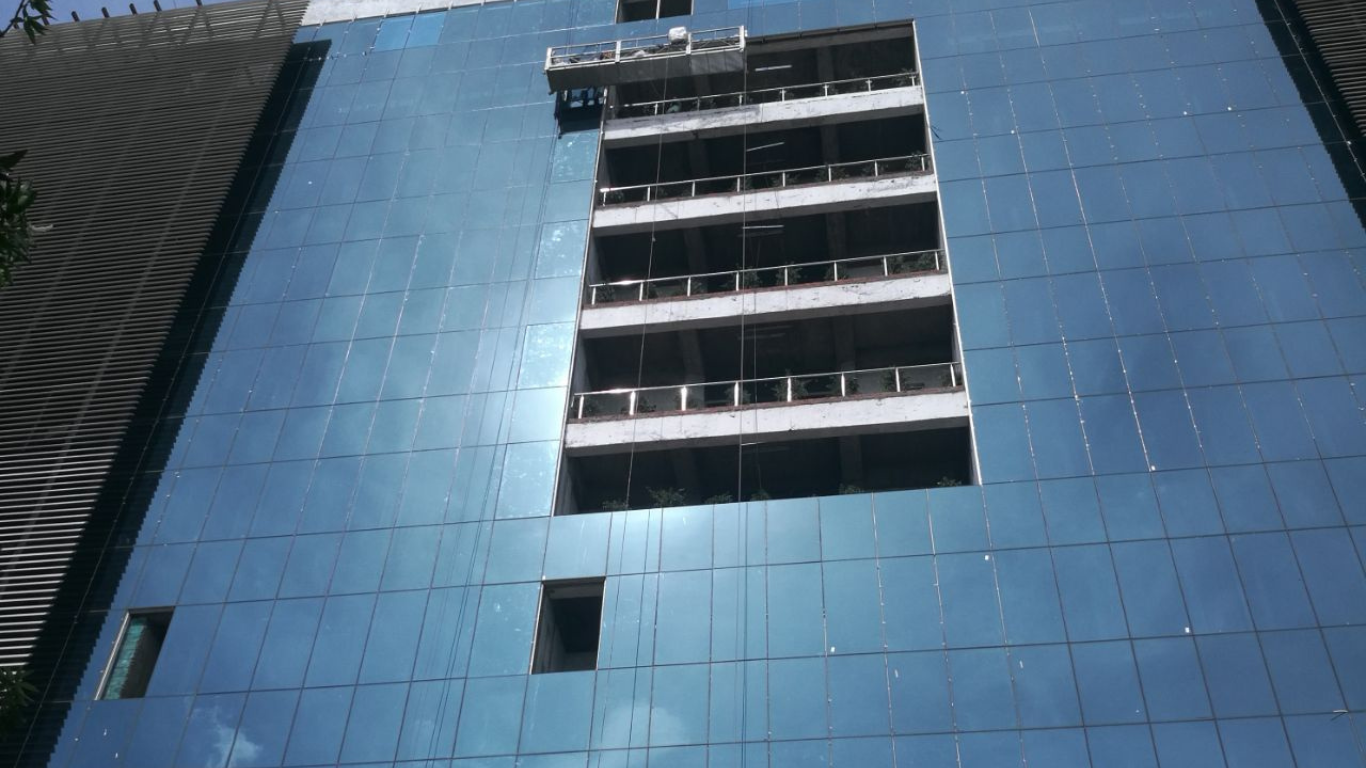
Facade engineering is a specialized field within architecture and construction that focuses on the design, performance, and integration of building facades. As the outer layer of a building, the facade not only contributes to the aesthetic appeal but also plays a critical role in energy efficiency, structural stability, and occupant comfort.
Facade engineering services are essential in ensuring that these elements work together effectively to create sustainable, functional, and visually striking buildings.
Scope of Facade Engineering Services
1. Design Development
Conceptual Design:
- Collaborate with architects and designers to develop a conceptual facade that reflects the building's identity and function.
- Utilize 3D modeling tools to create visualizations that help stakeholders understand design intentions.
Material Selection:
- Assess various materials (e.g., glass, metal, stone, composites) based on performance, durability, cost, and aesthetic value.
- Consider innovative materials, such as photovoltaic panels or dynamic shading systems, that enhance sustainability.
2. Performance Engineering
Thermal Analysis:
- Conduct thermal simulations to evaluate the facade's insulation performance and energy efficiency.
- Optimize designs to minimize heat transfer, reducing heating and cooling costs.
Structural Integrity:
- Perform structural analyses to ensure that the facade can withstand various loads, including wind, seismic activity, and weight of materials.
- Use software like SAP2000 or ETABS for detailed modeling and analysis.
Weather Resistance:
- Assess the facade's ability to resist moisture, air infiltration, and temperature fluctuations.
- Implement testing methods such as water penetration tests to verify design efficacy.
3. Regulatory Compliance
Building Codes and Standards:
- Ensure designs meet local, national, and international building codes, including safety, accessibility, and environmental regulations.
- Stay updated on changes in building regulations and industry standards.
Fire Safety:
- Evaluate materials for fire resistance and ensure compliance with fire safety codes.
- Design facades with appropriate egress routes and fire-rated assemblies.
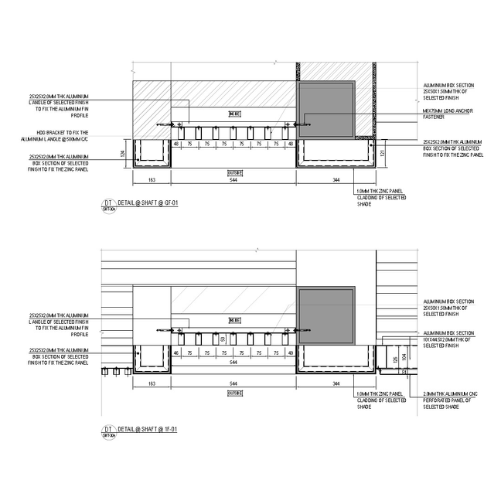
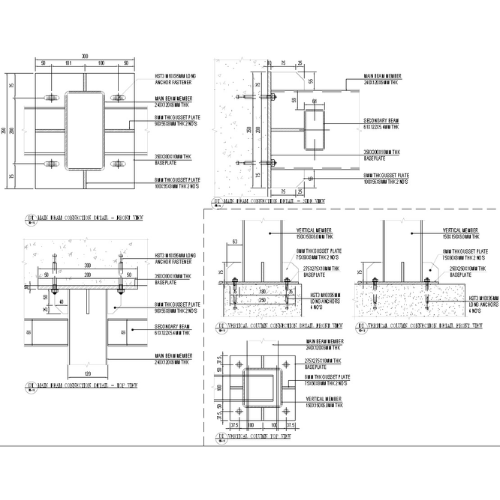
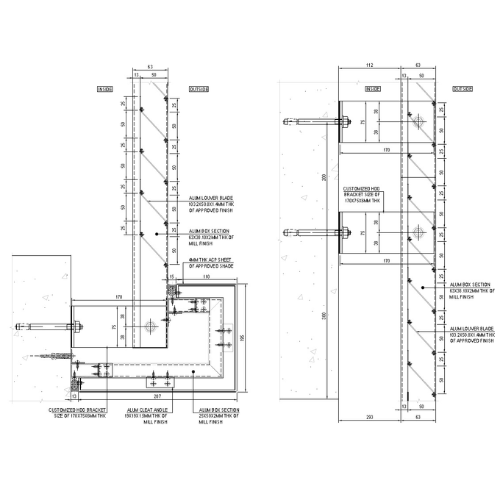
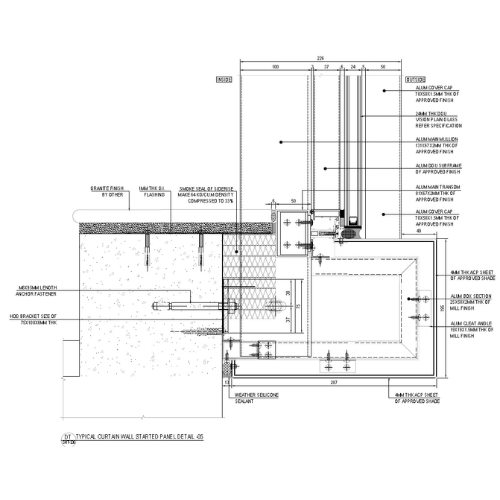
4. Construction Documentation
Detailed Drawings:
- Prepare comprehensive technical drawings and specifications that guide contractors during installation.
- Include information on materials, dimensions, finishes, and installation methods.
Mock-ups:
- Develop full-scale mock-ups to test the facade's aesthetics and performance before full installation.
- Conduct on-site tests for water resistance, air leakage, and thermal performance.
5. Project Management and Coordination
Interdisciplinary Coordination:
- Serve as a liaison between architects, structural engineers, and contractors to ensure seamless communication and collaboration.
- Facilitate design reviews and coordinate schedules among various teams.
Quality Assurance:
- Implement a quality control program to monitor construction processes, ensuring adherence to design specifications and industry standards.
- Conduct regular site inspections and provide detailed reports on progress and compliance.
6. Maintenance and Lifecycle Planning
Lifecycle Cost Analysis:
- Evaluate the long-term costs associated with materials and maintenance to inform design decisions.
- Propose solutions that balance initial costs with future maintenance and operational expenses.
Condition Assessments:
- Perform regular assessments of existing facades to identify signs of wear, damage, or inefficiencies.
- Recommend retrofitting solutions to improve performance or aesthetics, such as updating insulation or replacing glass.